Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer, NIO, announced that it had built more than 10,000 charging piles across China. The announcement came during the launch of the super-charging station at the Shuguang Technology Building in Shenzhen.
NIO launched its first destination charging station on August 22, 2018, in Chengdu, and since then the company has expanded its charging infrastructure across China’s landscape. Later on, in July 2019, the automaker established its first super-charging station in Suzhou.
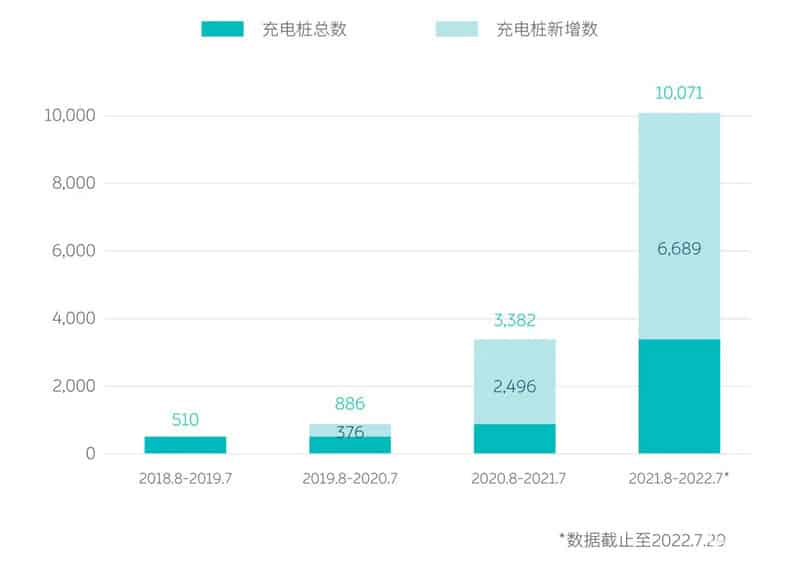
According to NIO, the exact number of charging piles built is 10,070, and they are spread across 269 Chinese cities. A breakdown of the figure shows that there are 936 supercharging stations with a combined total of 5,091 super-charging piles. These super charging piles make up over 50% of the total number.
There are also 4,980 destination charging piles. The automaker stated that as of July 29, it had erected 1,039 battery swap stations across China with 264 of them on the expressway.
NIO’s largest super-charging station, located in Shenzhen Futian Abe Watt has 80 supercharging piles, and can charge up to 2,000 cars daily.
Unlike most automakers, NIO opens up its charging piles to all NEVs, and 80% of the energy is consumed by non-NIO brands.
Additionally, the company noted that the charging stations had provided over 9.6 million charging services at the rate of 30,000 daily on average.
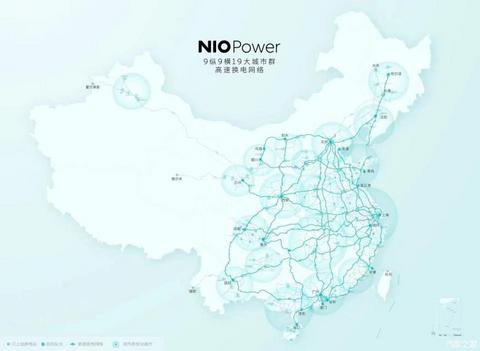
During the 2022 NIO Power Day held on July 6, the automaker had revealed plans to develop a high-speed power exchange network spanning across 19 urban clusters and nine north-south/nine east-west highways.
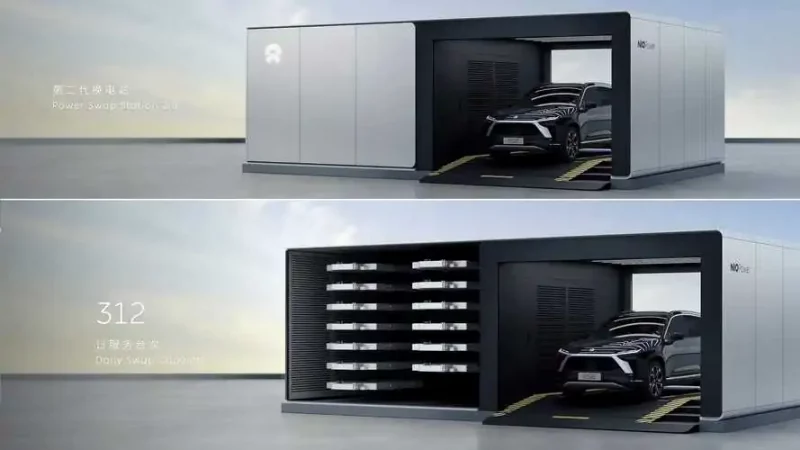
Additionally, the firm had promised to develop its third-generation battery swap stations and advanced supercharging piles by the end of the year. The supercharging piles will be able to churn out a peak power of 500 kW and 650A peak current.
The company continues to work towards its goal of building at least 4,000 swap stations globally by 2025. Only recently, it announced plans to open a battery station plant in Hungary by September.
Sources: First electric network, Sina